MESA Communication Standards and Specifications
The Modular Energy System Architecture (MESA) Standards Alliance is an industry association of electric utilities and technology suppliers. MESA’s mission is to accelerate the interoperability of distributed energy resources (DER), in particular utility-scale energy storage systems (ESS), through the development of open and non-proprietary communication specifications, based on standards. MESA has developed and published two specifications: the MESA-DER Specification based on DNP3 with IEC 61850 data objects, and the MESA-Device/SunSpec Smart Storage Specifications. MESA-DER is now becoming the IEEE 1815.2 standard.
MESA Announces MESA-DER Testing and Certification.
Join us in transforming the energy system market.
MESA has developed two communications specifications for Distributed Energy Resources (DER) and Energy Storage
MESA-DER DNP3 Data Model Becoming the IEEE 1815.2 Standard
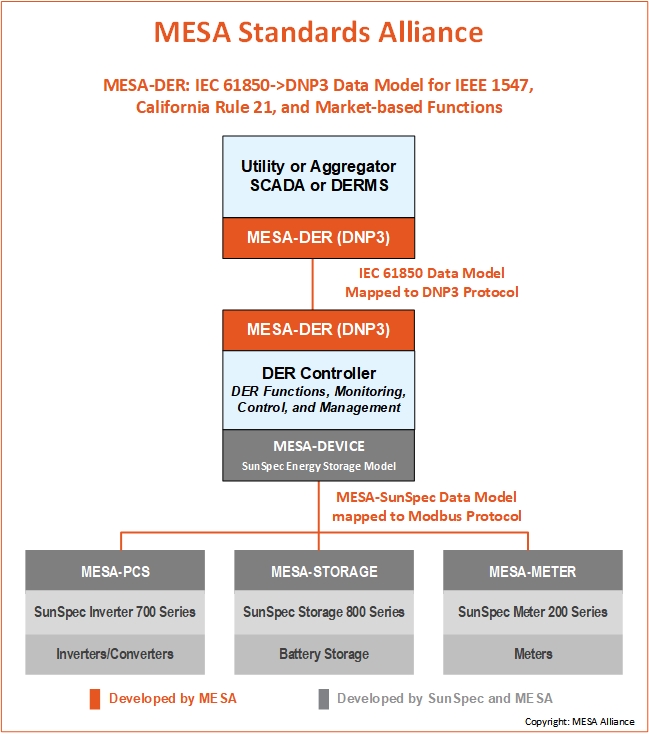
The MESA-DER DNP3 data model provides interoperable communications for Distributed Energy Resources (DER) with a special focus on utility-scale energy storage system (ESS). It combines two international standards: IEC 61850 and IEEE 1815 (DNP3) by mapping the IEC 61850-7-420 semantic data object standard for DER to the widely-used IEEE 1815 (DNP3) protocol standard, thus creating an interoperable profile of DER functions, monitored information, and control commands. MESA-DER supports all the IEEE 1547 and California Rule 21 DER functions as well as additional market-based DER functions to support utility grid safety, reliability, and efficiency operations. In addition, MESA-DER covers the data exchange requirements for ESS configuration management, including ESS role-based access control (RBAC) for different ESS operational states. The MESA-DER mapping is defined in the DNP3 Application Note AN2018-001 and is becoming IEEE 1815.2 (balloting expected in early 2024).
MESA-Device Specifications/SunSpec Energy Storage Model
Addresses how energy storage components within an energy storage system communicate with each other and other operational components. MESA-Device specifications are built on the Modbus protocol.
About MESA Standardized Specifications
Utility grid technologies are undergoing a rapid evolution in response to changes in how power is being deployed on the electricity grid today.
Changes from the last decade include the integration of renewable energy sources, the addition of energy storage, and the bi-directional flow of energy between the grid and distributed energy resources (DER).
The adoption of open and standardized specifications simplifies the integration of these technologies and increases the pace of their deployment in grid applications.
MESA members include utilities and energy storage solution providers who work together to build interoperability into their products and ensure they are architected for grid integration.
As a MESA member, you can participate in MESA working groups to guide the development of MESA specifications, learn how to incorporate MESA specifications into your products and/or control systems, and share knowledge with your peers.
Open Standards for Energy Systems
MESA specifications support safe, affordable, and scalable energy systems, including storage
Benefits for Everyone
- Reduce costs of technology deployment
- Reduce risk by enabling supplier flexibility
- Simplify long-term maintenance and system upgrades
- Efficiently scale energy storage deployments
- Reduce training costs and compliance testing costs
- Provide products designed for integration with other MESA-compliant products
- Increase the array of available partners for projects
- Focus resources on making your product better, rather than on system integration
- Streamline deployments and meet customer timelines
- Use international communication standards, including IEEE 1815 (DNP3), IEC 61850, and Modbus
- Meet all interoperability requirements for IEEE 1547 DER interconnection standard

